Otoacoustic Emissions (OAE) are sounds generated by the inner ear, specifically the outer hair cells of the cochlea, in response to an acoustic stimulus.
Spontaneous OAE (SOAE): Emissions that occur without any external stimulation.
Evoked OAE (EOAE): Emissions that are elicited by an external acoustic stimulus, such as clicks or tones.
OAE testing is commonly used in audiology to assess the function of the cochlea and outer hair cells.
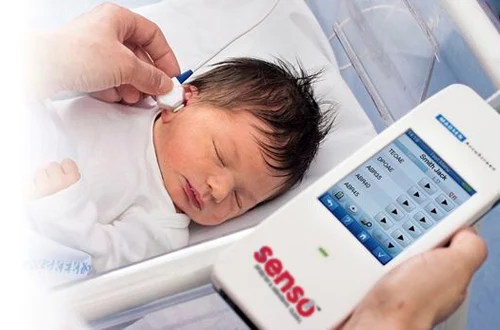
It is particularly useful in newborn hearing screenings and in identifying hearing loss, especially in infants and young children.
Newborn Hearing Screening: OAE testing is often part of the newborn hearing screening protocol to identify potential hearing issues early.
Diagnostic Testing: OAEs can be used diagnostically to assess the integrity of the cochlea and to differentiate between sensorineural and conductive hearing loss.
During OAE testing, a small probe is placed in the ear canal, and sounds are presented through the probe. The emissions generated by the inner ear are then recorded and analyzed.